| Satellite | ACS3 (Advanced Composite Solar Sail System) |
|---|---|
| Form factor | CubeSat |
| Units or mass | 12U |
| Status | Operational (Press release on 2024-08-29 about sail deployment) |
| Launched | 2024-04-23 |
| NORAD ID | 59588 |
| Deployer | EXOpod Nova 12U/16U [Exolaunch] |
| Launcher | Electron |
| Organisation | NASA Ames Research Center |
| Institution | Space agency |
| Entity | Government (Civil / Military) |
| Nation | US |
| Manufacturer | AIVT by NanoAvionics |
| Launch brokerer | Rocket Lab |
| Oneliner |
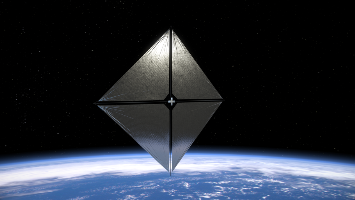
Characterize solar sail structures technologies for future small spacecraft deep space missions. |
| Description |
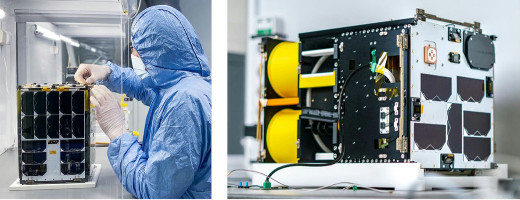
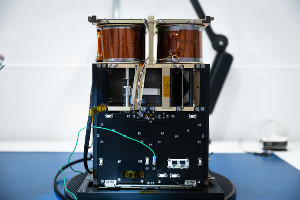
An approximately 800 square foot (74 square meter) composite boom and solar sail system. The aim of the ACS3 mission is to replace conventional rocket propellants by developing and testing solar sails using sunlight beams to thrust the nanosatellite. These solar sail propulsion systems are designed for future small interplanetary spacecrafts destined for low-cost deep-space and science missions requiring long-duration, low-thrust propulsion. As part of this agreement the company will also supply a mechanical testbed model and a FlatSat model. In addition, a team of NanoAvionics engineers will provide the support required for testing, integration and operations of the nanosatellite. The FlatSat model has identical software functionality as the final 12U bus hardware, hosting the actual payload. It allows NASA Ames to run tests via remote network connectivity without having to ship equipment back and forth. The mechanical testbed model can be used for testing payload integration and other mechanical tests, such as the deployment of solar sails. |
| Results | |
| Sources | [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] |
| Photo sources | [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] |
| COTS subsystems |
|
| Keywords | Solar sail |
Last modified: 2024-12-14