| Spacecraft | LaCE |
|---|---|
| Form factor | CubeSat |
| Units or mass | 3U |
| Organisation | Naval Information Warfare Command (NIWC) Pacific |
| Institution | Military |
| Entity type | Government (Civil / Military) |
| Country | US |
| Launch brokerer | SEOPS |
| Oneliner |
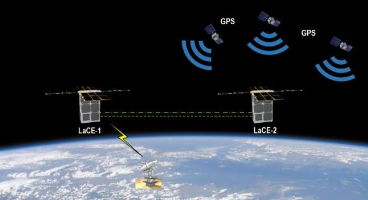
Demonstrate a low SWAP optical communications crosslink in LEO (Low Earth Orbit). |
| Description |
Demonstrate a low SWAP optical communications crosslink in LEO (Low Earth Orbit). |
| Results | |
| Sources | [1] [2] [3] [4] |
| Photo sources | [1] |
| Keywords | Laser transmitter, License Plate Identification Tag |
Related Spacecraft
| Satellite | Status | Rocket | Date | Orbit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LaCE 1 (Lace A, LaCE-1, Laser Crosslink Experiment) | Operational (SmallSat 2024 and CDW 2025 presentations) | Falcon 9, (Transporter-10) | 2024-03-04 | 510 km, 97.5 deg |
| LaCE 2 (Lace B, LaCE-2, Laser Crosslink Experiment) | Was operational until 2024-03-13 (CDW 2025 presentation) | Falcon 9, (Transporter-10) | 2024-03-04 | 510 km, 97.5 deg |
Last modified: 2025-04-27